COVID-19
At the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, depression, and anxiety levels increased by a staggering 25% worldwide (source). Multiple stressors influenced this, including loneliness, financial concerns, death of loved ones, and burnout in healthcare workers, among other factors. Women were among the most severely affected by the pandemic. Women with risky alcohol use during the pandemic were also found to have higher anxiety and depression compared to those with low-risk use. Women are becoming increasingly likely to use substances, as shown by the increasing alcohol sales and opioid overdoses during the pandemic (source).
The infectious respiratory disease Coronavirus 2019, or COVID-19, continues to be studied, and new information and updates about long-term effects are being released. COVID-19 data regarding cases, deaths, and current vaccinations are released daily on MDH’s website. For comprehensive information on the impacts of COVID-19 on rural MN, look to the Center for Rural Policy’s report, which explores the data, access to health care, and impacts on the economy and workforce.
Sources for graphics: (above)
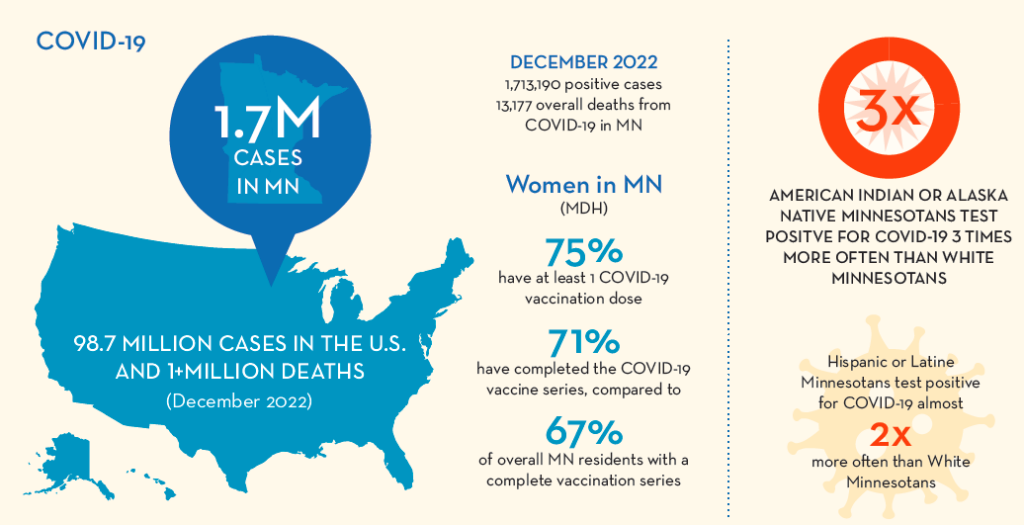
- 1,713,190 total positive cases, including reinfections (MN, December 2022)
- 13,177 overall deaths from COVID-19 (MN, December 2022)
- 98,700,000 total positive cases (U.S., December 2022)
- 1,090,000 total deaths from COVID-19 (U.S., December 2022)
- 74.9% of MN women have at least one COVID-19 vaccination dose (MN, December 2022)
- 70.9% of MN women have completed the COVID-19 vaccine series, as compared to the state total of 66.4% of MN residents (December 2022)
MN Race and Ethnicity COVID-19 Data (per 100,000 people)
This scaling allows for the outcome of cases or deaths from COVID-19 to be compared to the size of each population group (March 2021 via The COVID Tracking Project).
| Race and Ethnicity | Number of Cases per 100,000 People |
| Black or African American | 10,952 |
| Hispanic or Latino | 14,619 |
| Asian | 8,006 |
| Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander | 25,342 |
| American Indian or Alaska Native | 7,988 |
| White | 7,110 |
| Race and Ethnicity | Number of Deaths per 100,000 people |
| Black or African American | 89 |
| Hispanic or Latino | 68 |
| Asian | 97 |
| Native American or Other Pacific Islanders | 273* |
| White | 118 |
More information about COVID-19 can be found on the MDH and CDC websites.
Mpox
Mpox, previously known as Monkeypox, is a viral illness that anyone can get regardless of sexual orientation or gender identity. Mpox cases did not normally occur in the U.S. until May 2022. Mpox symptoms often include a blister-like rash that can appear on various areas of the body (source).
- 234 cases of Mpox have been identified in MN as of December 2022
- 6 cases (3%) are women, 4 cases (2%) are transgender men
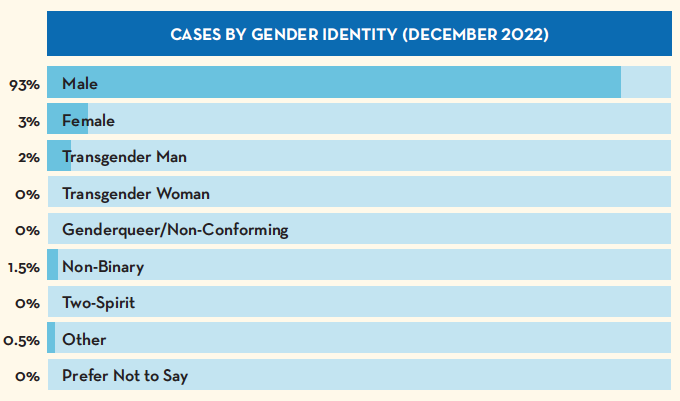
10 cases have been hospitalized, and there have been no deaths associated with Mpox thus far in Minnesota (January 2023, source).

More information about Mpox can be found on the MDH website.