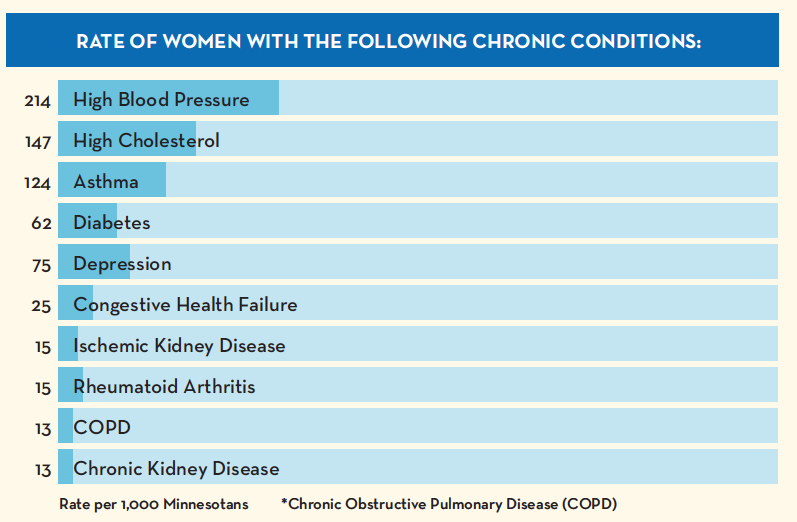
Chronic diseases place a burden on individuals and families in MN. These burdens are unevenly distributed across populations and areas of the state. Older, rural, 2SLGBTQIA+ Minnesotans bear a higher burden of chronic disease. The prevalence of chronic conditions for Minnesotans 60+ has been increasing since 2009. About 76% of Minnesotans 60+ have at least one chronic condition. Obesity and hypertension also increase across MN populations aged 18-64 (source).
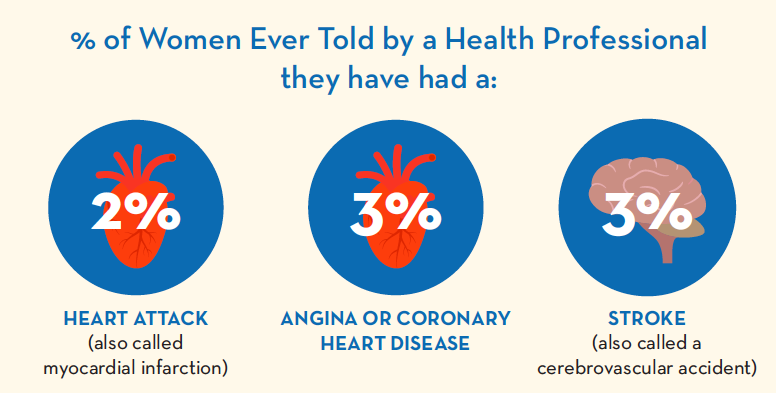
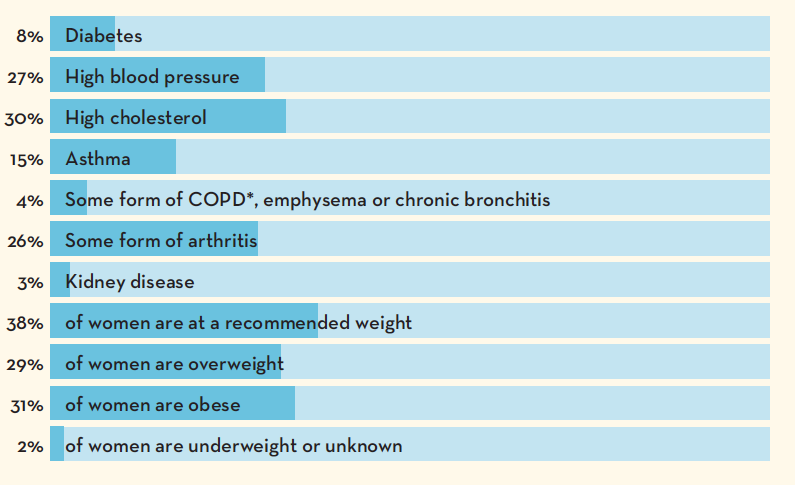
(source)
Chronic Disease in Minnesotan Lesbian, Gay, and Bisexual (LGB) Women
Overall findings (source):
- Adults that identify as lesbian, gay or bisexual (LGB) living in rural locations have the highest rates of chronic conditions overall (43.8% for rural LGB adults).
- The rates of chronic conditions in both rural and urban locations are higher for adults that identify as LGB compared to adults that identify as heterosexual.
| % of Individuals Identifying as LGB That Have Been Told They Have: | Urban Settings | Rural Settings |
| Arthritis | 36.4 | 29.4 |
| Asthma | 14.7 | 29.2 |
| COPD | 5.6 | 6.4 |
| Heart disease | 2.1 | 2.1 |
| Diabetes | 4.8 | 12.3 |
| Had a heart attack | 1.5 | 3.0 |
| High blood cholesterol | 17.6 | 21.0 |
| High blood pressure | 20.8 | 31.8 |
| Had a stroke | 1.8 | 1.9 |
Chronic Disease Mortality
- African American and Asian American women died from stroke 40% more than White women (source)
- Native American women die from heart disease 52% more often than White women (source)
- 59 women died due to asthma (source)
- 367 died due to heart attack (source)
- 5,953 died due to heart disease (source)
- 647 died due to diabetes (source)
- 354 died to due chronic liver disease and cirrhosis (source)
- 250 died due to renal failure (source)